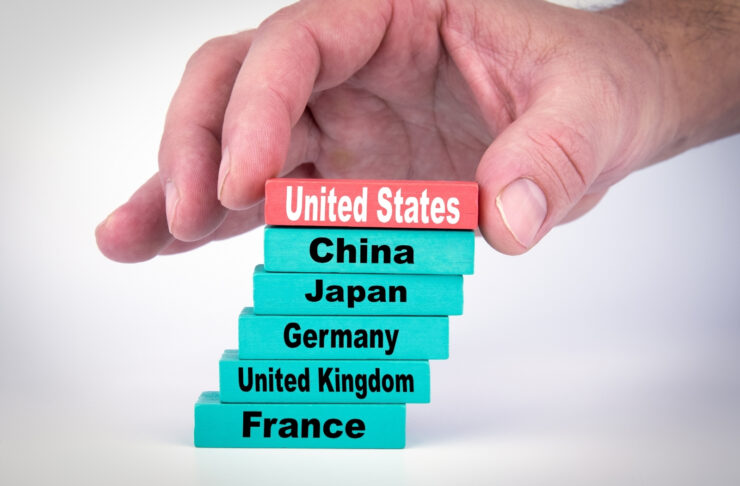
The ranking of the world’s biggest economies relies on the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of every nation. GDP is an approximation of the sum of a country’s refined goods and services produced over a given period, typically a year. GDP is measured using the expenditure method.
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has adversely affected the global economy. Before the pandemic struck, Brazil was among the top biggest economies of the world. India was fifth, South Korea wasn’t even in the top ten categories. After the aftermath of the COVID, this is how countries now appear in the list of the top 10 biggest economies in the world:
United States
The United States’ sophisticated technology and advanced service sector account for about 80% of the country’s total output. For this reason, with a 20% global output, the US economy remains large even when compared to China. US corporations lead in technology, healthcare, retail, and finance gives the US a pivotal role on the world stage. According to the nominal GDP of 2019-2020, the US economy exceeded 21 trillion USD. Despite maintaining the highest GDP, the United States has however been adversely affected by the pandemic thanks in part to state lock-downs and limited travel.
China
In 2019, China’s nominal GDP was 14.14 trillion USD. The country’s economy has experienced astounding growth in the last few decades. From the advancement in various industries, China attained the desired second rank in the ten big economies categories in the world.
China was the first to experience the COVID-19 pandemic. This fact enabled the country to wave through the pandemic quickly and get its economy back on track before the rest of the world. China is an export-led country, with a high demand placed on medical equipment and consumer goods, its GDP is continuously on the rise.
Japan
Japan experienced rapid economic growth in 1960, the 70s, and 80s but slowed in the 1990s. Since then, Japan has worked to grow its economy over the last ten years. In 2019-2020, Japan’s economy was ranked third with a nominal GDP of 5.15 trillion USD. Despite the pandemic, Japan’s economy aims to have a moderate growth of 3.42% for its next fiscal year.
Germany
The nominal GDP of Germany in 2019-2020 was about 4.2 trillion USD, making it the fourth-biggest economy in the world. Germany has since had a rebound of 4.0% growth. Germany has recovered remarkably from its 2000-2009 tumbled economy. Consistent growth has been experienced over the years, maintaining its fourth place even during the pandemic. About 5% of Germany’s economy has been affected by the pandemic. Thanks to containment measures have been successful, there is a possible economic rebound in 2022.
United Kingdom
With 3.2 trillion USD in nominal GDP in the 2019-2020 fiscal year, The UK places fifth in the list of ten big economies in the world. This position came after India fell out to position six due to a ravaged economy from the pandemic. The UK recorded an average growth of 2.8% in the years between 1999 and 2008. The following years had a drop in economic growth due to BREXIT uncertainties. Also, the economic tensions brought about by the pandemic have grievously impacted BREXIT.
India
India was all set for position five after overtaking France in 2018 before the COVID-19 pandemic hit. India’s nominal GDP was 2.9 trillion USD in the 2019-2020 fiscal year, ranking it in the sixth position. The country ranked among the world’s fastest-growing economies. According to an IMF data analysis done by CNBC, India expects to regain a fifth place in the top ten world’s biggest economies by 2023. A contraction of about 8% was likely before the country started battling its third wave of the pandemic.
France
France’s GDP originates from the service sector and automotive arenas, aerospace, and railway. With a record of 2.9 trillion USD nominal GDP, France was ranked the seventh biggest world economy at the close of 2019-2020 fiscal year. From the onset of COVID-19, the total output of the French economy was slashed by 8%. A Contraction of about 1.3% of the economy has been recorded in the last quarter of 2020.
Italy
Italy is the eighth biggest world economy with a nominal GDP of $2.0 trillion USD. Growth of up to 0.3% of the country’s economy has been observed since 2018. Italy has a divided economy with underdeveloped southern regions and developed northern regions. The inefficient court system, high public debts, and high youth unemployment are reasons Italy records slow economic growth. Italy’s GDP has also been affected by COVID-19, but an approximate 4.1% growth is projected for 2021 and similarly for 2022.
Canada
Canada is an energy superpower, with the third-highest approximated value of natural resources worth over $33.2 trillion in 2019. Also, the country is ranked ninth in the world’s biggest economies with a nominal GDP of 1.978 trillion USD. Despite an economic drop of 7.1% observed in 2020, there has been a 5.2% projected growth in 2021.
South Korea
As the average world GDP dropped due to COVID-19, South Korea managed to scoop the tenth position in the list of the world’s biggest economies. The rank came after Brazil fell out of the top ten big economies to twelfth place. South Korea had a nominal GDP of 1.8 trillion USD in 2020. In 2019, South Korea had a growth rate of 2.0%, followed by a drop of 1.1% in 2020. South Korea was among the first nations to deal with the pandemic, coming out of it earlier and now projects a growth of 3.2% in 2021.
While countries are still recovering from the effects of COVID-19, the pandemic still poses a risk to the world’s biggest economies even amidst vaccinations. The top ten world global economies may keep on fluctuating as the virus continues to cripple the various economies.